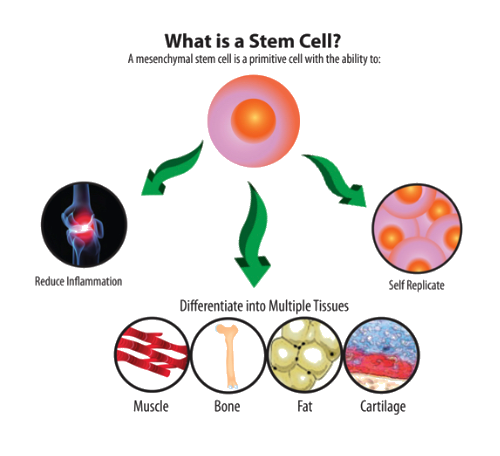
What is a Stem Cell?
What is a stem cell, you ask? Essentially, a stem cell is any cell that has the ability to self-replicate and differentiate. Differentiation is the process by which stem cells are able to convert into various types of tissue, making these cells highly valuable in the treatment of injuries and degenerative conditions. While there are many types of stem cells, therapeutic applications most commonly use what are known as “adult stem cells.” These cells exist within various adult tissues including bone and subcutaneous fat.
Bone Marrow Stem Cells
Bone marrow stem cells are one of many types of autologous stem cells, meaning they are found within adult tissues. These cells are derived from the patient’s bone marrow via aspiration and are classified as adult mesenchymal stem cells. Because mesenchymal stem cells are undifferentiated, they have the ability to self-renew and differentiate into multiple types of specialized tissues. The use of bone marrow stem cells is dependent on the condition being treated as well as the age of the patient.
 Adipose Stem Cells
Adipose Stem Cells
Adipose stem cells are one of several types of autologous stem cells. These cells are taken from each patient’s adipose tissue and are typically collected from around the patient’s abdomen via a simple aspiration procedure. They are classified as adult mesenchymal stem cells, demonstrating the ability to differentiate into a wide range of specialized cells. Their primary advantage over stem cells sourced from other tissues such as bone marrow, is that they are easily harvested using minimally-invasive techniques. Adipose tissue also contains higher concentrations of stem cells than other tissue types; however, the use of adipose stem cells is dependent on the condition being treated as well as the age of the patient.
Cord Blood Stem Cells
Umbilical cord blood contains concentrated numbers of mesenchymal stem cells, hence, the popularity of cord blood banking. Cord blood stem cells are collected from umbilical cord tissue and donated following live, healthy births. They are immediately cryopreserved and reserved for future use. These cells are classified as mesenchymal stem cells, demonstrating the ability to self-renew and differentiate into multiple specialized tissue types.
At Nona Medical Arts, we offer several restorative treatment options to address chronic pain at its source. Depending on the type and severity of your condition, you may be a candidate for our customized treatment approach. Our knowledgeable and experienced practitioner will conduct a thorough evaluation of your condition and based on our findings, will recommend the appropriate treatment option(s). If you think you may be a candidate for treatment or would like to learn more, contact our office to schedule your complimentary consultation.
How do adult stem cells promote healing?
Because stem cells possess the unique ability to differentiate into various tissues, they have the capacity to restore tissues in areas of injury or degeneration. Essentially, when a stem cell detects a dying or dysfunctional cell, it then divides to form two copies of itself — one is another stem cell, and the other is known as a progenitor cell. The progenitor cell is essentially a more specialized version of the stem cell, which then differentiates into the type of cell that must be replaced. Over time, as these cells continue to replace dying and damaged cells, tissue restoration is experienced.
What conditions can be treated?
Restorative treatments are handled on a case-by-case basis as this type of treatment requires a highly-individualized approach. After an extensive evaluation, the practitioner will then determine if you may be a candidate for restorative treatments. During your consultation, you will have the opportunity to discuss both the potential risks and benefits of treatment, along with any concerns you may have regarding the procedure. It is important that you possess medical imaging of the intended treatment area so that the practitioner may perform a thorough analysis of your condition.
Commonly-treated conditions include:
• Neck, back and spine pain
• Degenerative joint conditions
• Tendonitis

