Stem cells have become a popular topic in the medical world due to their potential to treat a variety of diseases and conditions.
One such condition is degenerative osteoarthritis, a condition that affects the joints and bones and can cause pain and disability.
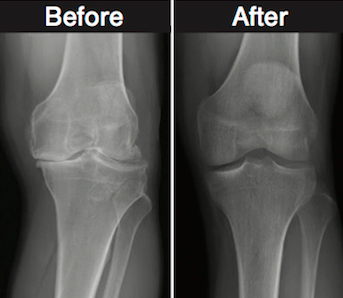
Recent research has shown that stem cells may be able to help treat this condition, offering hope to those who suffer from it.
Stem cells are capable of self-renewal and can differentiate into a variety of cell types.
This means that they can be used to replace damaged cells and tissues, as well as to stimulate the body’s own healing response.
This makes them a promising therapy for degenerative osteoarthritis, which is caused by the breakdown of cartilage in the joints.
Recent studies have shown that stem cells can be used to regenerate cartilage in the joints of patients with degenerative osteoarthritis.
The stem cells are injected directly into the joint, where they can stimulate the body’s own healing response and help to regenerate the damaged cartilage.
This can reduce pain and improve mobility in the affected joint.
Another potential use for stem cells in the treatment of degenerative osteoarthritis is to reduce inflammation.
Studies have shown that stem cells can reduce inflammation in the joints, which can help to reduce pain and improve mobility. This could be a valuable tool for those suffering from this condition.
Finally, stem cells may also be used to help regenerate bone in the joints.
This could be especially helpful for those with severe degenerative osteoarthritis, as it could help to restore joint function and reduce pain.
Overall, stem cells are a promising therapy for degenerative osteoarthritis. They have the potential to reduce pain, improve mobility, and even help to regenerate damaged cartilage and bone.
While more research is needed to fully understand the potential of stem cells for this condition, the results so far are encouraging.
Read more about degenerative disc disease